

These changes will be inherited by future generations if they occur in eggs, sperm or their cellular precursors (the germline).

DNA image via Mutations are changes to the letters of DNA’s genetic code – for instance, a nucleotide Guanine (G) becomes a Thymine (T). Mutations are changes to the DNA code, such as when one nucleotide base (A, T, G or C) is incorrectly subbed for another. By applying these methods to the ever-growing database of DNA from diverse populations (both present-day and ancient), geneticists are helping to build a more refined timeline of human evolution. Molecular clocks are becoming more sophisticated, thanks to improved DNA sequencing, analytical tools and a better understanding of the biological processes behind genetic changes.

These changes accrue like the ticks on a stopwatch, providing a “molecular clock.” By comparing DNA sequences, geneticists can not only reconstruct relationships between different populations or species but also infer evolutionary history over deep timescales. Because certain genetic changes occur at a steady rate per generation, they provide an estimate of the time elapsed. Moreover, relevant fossils or artifacts have not been discovered for all milestones in human evolution.Īnalyzing DNA from present-day and ancient genomes provides a complementary approach for dating evolutionary events. However, these methods require ancient remains to have certain elements or preservation conditions, and that is not always the case.
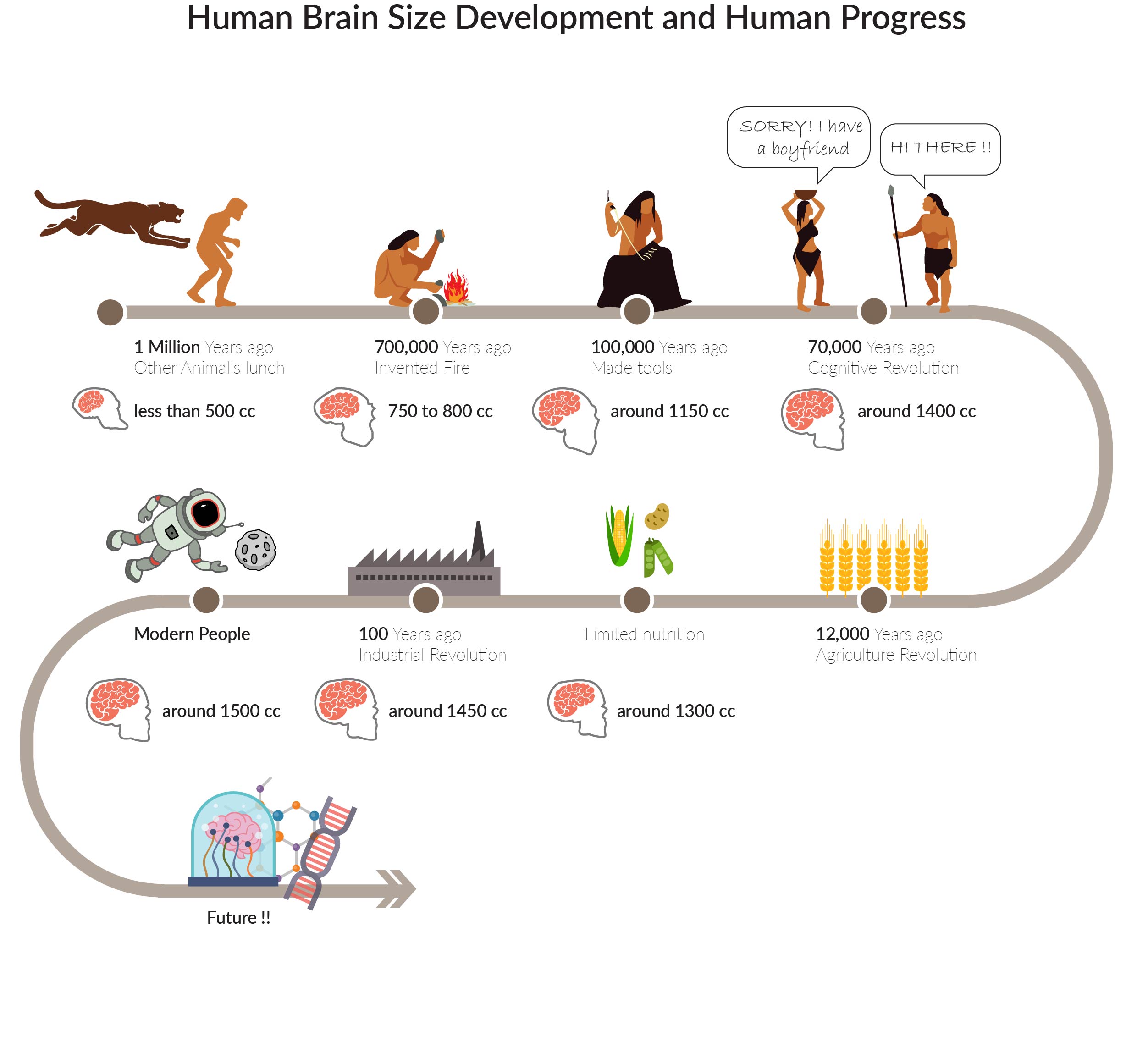
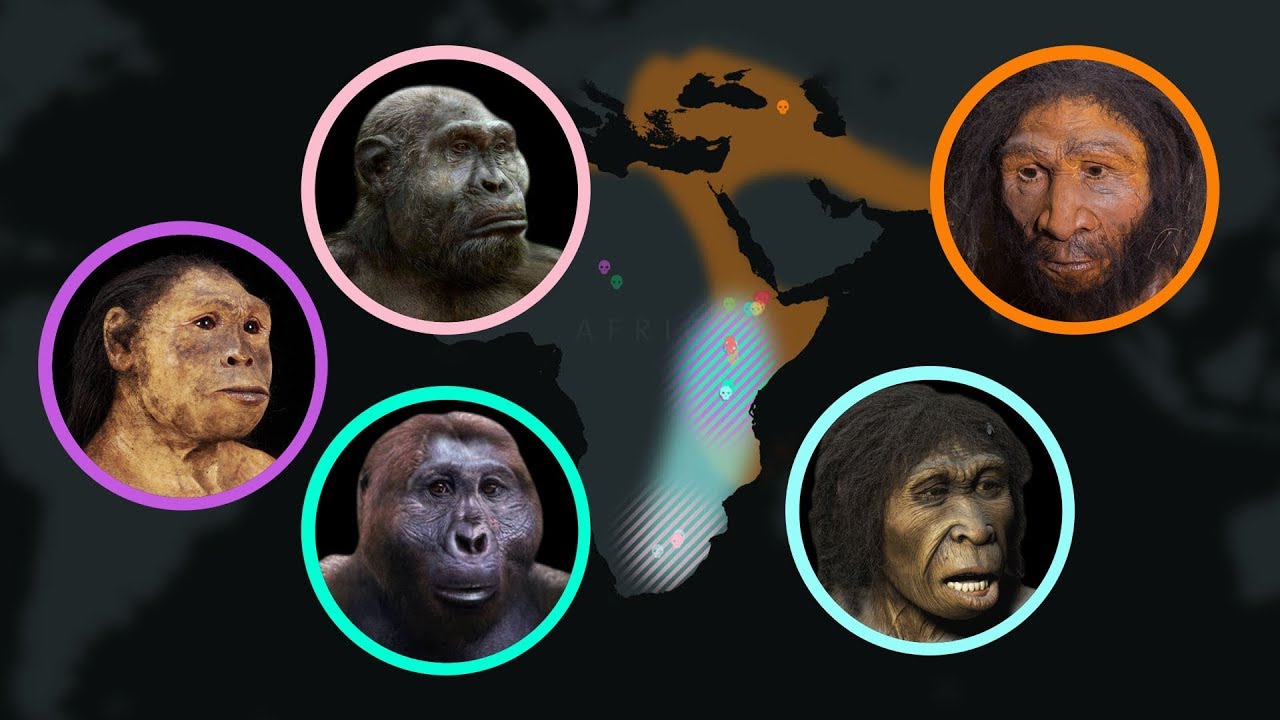
When scientists say that modern humans emerged in Africa about 200,000 years ago and began their global spread about 60,000 years ago, how do they come up with those dates? Traditionally researchers built timelines of human prehistory based on fossils and artifacts, which can be directly dated with methods such as radiocarbon dating and Potassium-argon dating. And our DNA also holds clues about the timing of these key events in human evolution. DNA holds the story of our ancestry – how we’re related to the familiar faces at family reunions as well as more ancient affairs: how we’re related to our closest nonhuman relatives, chimpanzees how Homo sapiens mated with Neanderthals and how people migrated out of Africa, adapting to new environments and lifestyles along the way.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
